ISC is an annual global event in which high performance computing (HPC) users and technology providers come together to discuss the prospects of HPC in different areas. One particular area that concerns us all is weather forecasting. In recent years, the demand for greater precision in weather forecasting has increased significantly. The development of HPC plays an important role in this process.
Challenges and Requirements
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) is a technique used to predict the atmospheric motion and weather events over a certain period of time. Its prediction flow involves collecting meteorological observation data, pre-processing data, performing model computing, and post-processing data. Model computing is a typical HPC application that is characterized by intensive I/O + computing, and demands high compute, network, and I/O performance of HPC clusters. The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) system is shown below:
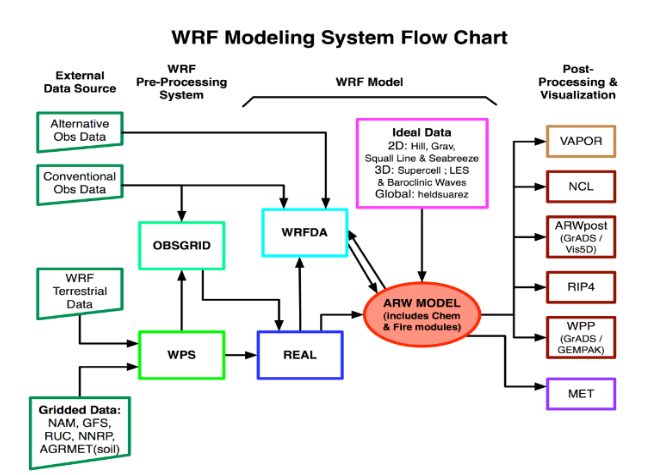
WRF Modeling System Flow chart
As the volume of weather data continues to grow, weather forecasting raises increasingly diverse and demanding requirements in terms of data storage and I/O performance. The following aspects highlight the need for enhanced capabilities:
- Data collection: Terabytes and even hundreds of terabytes of data are collected through radars, observation stations, and satellite remote sensing, etc., requiring high-bandwidth processing of large files.
- Data pre-processing: The weather change process requires hybrid workloads of high bandwidth and medium-level IOPS.
- Model computing: Large file small I/O and large file large I/O hybrid read and write is required to solve equation sets using concurrent computing and high-performance storage capabilities.
- Data post-processing: Large file small I/O random read and sequential write as primary mode is required for visualizing model computing results to present to experts. This also requires high IOPS performance (> 100K).
- Presentation: Presenting results on terminals (such as internet) in the form of image, animations, and web pages needs sequential write and random read as primary mode, for which lower I/O performance suffices.
Weather Forecasting Development with Huawei OceanStor Pacific Scale-Out Storage
Huawei launched OceanStor Pacific Scale-Out Storage to meet these requirements and deliver highly scalable, high-performance, and high-reliability PB-level data services for NWP and application software systems. This was developed after careful analysis of customers’ business needs and I/O patterns of business software.
OceanStor Pacific Scale-Out Storage offers the following advantages:
- Advanced architecture: all-symmetric scale-out architecture, supporting online capacity expansion and upgrade to fit expansion requirements over the next 5 years.
- Hybrid workloads and high-performance I/O concurrency: supporting high bandwidth and IOPS within one storage system, allowing data private clients (DPC) to combine with MPI-I/O, and fitting concurrent I/O requirements of NWP.
- Unified data foundation: One storage system meets the data collection, primary model computing, post-processing, and data services requirements. It also offers 35% quicker processing because it supports file, object, and big data interfaces through tiering software without needing to copy data. In addition, one storage system supports SSDs, HDDs, and Blu-ray storage, providing smooth application services with SSD-level performance and HDD-level space usage, slashing CAPEX by 40%.
- Data resilience protection: all-proprietary compute, network, storage, and management software, fully ensuring information resilience.
Innovation-Driven NWP
Science and technology transform industries, as demonstrated by the NWP efficiency improvement Huawei OceanStor Pacific Scale-Out Storage delivers:
- Improved WRF model storage access performance: DPC combining with MPI-I/O is able to fully distribute workloads to every I/O node and improve forecast accuracy performance by almost 10 times within an area of 1 km.
- Significantly improved task efficiency in large-scale cluster environments: Computing time decreases with an increase in computing nodes. Furthermore, the overall time decreases by 1/3 compared to before in an environment with 64 nodes and 40 cores for each node. This is thanks to I/O performance improvement.
- Improved data search efficiency: A metadata-driven data organization and management system adheres to industry data standards and regulations, and user needs. This system uses metadata search functions, greatly improving data search and management efficiency.
Weather forecasting plays a crucial role in our daily lives. One small improvement in forecast accuracy can have a significant impact on society. Science and technology innovations can change the world. Huawei is committed to advancing HPC application in fields such as weather forecasting with the goal of driving meaningful change.





